|
SUPPORT
Fuse selection process
1. Safety certification: The safety certification of the fuse is determined according to the safety certification required by the whole machine, such as UL specifications or IEC specifications.
2. Structural size: The size of the size is determined according to the space in the circuit design, such as length, diameter, whether with leads, etc.
3. Rated voltage: must be greater than or equal to the actual application voltage, generally 24V, 32V, 63V, 125V, 250V, etc.
4. Breaking capacity: should be greater than the maximum fault current in the circuit.
5. Rated current: refer to the following items:
(1) The normal working current is operated at 25°C; the rated current of the UL specification fuse is greater than or equal to the normal operating current/0.75; the rated current of the IEC specification fuse is greater than or equal to the normal operating current/0.9.
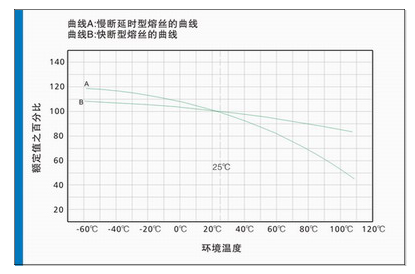
(2) Ambient temperature: The current carrying capacity test of the fuse is carried out at an ambient temperature of 25°C. The higher the ambient temperature, the shorter the life of the fuse and the lower the carrying capacity. Therefore, the ambient temperature and The effect of temperature on the current carrying capacity is shown in the figure below:
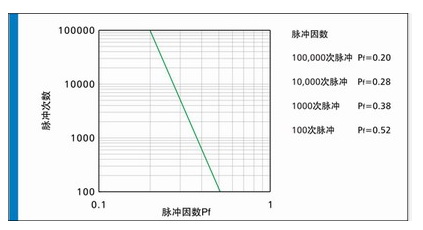
(3) Pulse: Pulse will generate thermal cycle and produce mechanical fatigue that will affect the life of the fuse. In the design, the pulse I2T should be smaller than the nominal melting heat energy I2T of the fuse under the premise of considering the pulse factor; the rated I2T of the fuse> the actual pulse I2T/Pf; Pf: pulse factor, which varies according to the number of pulses it can withstand. The specific value is shown in the figure below:
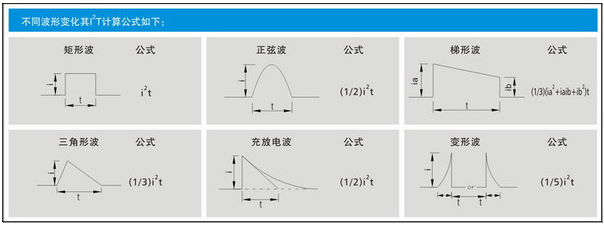
6. Test
Samples selected through the above procedure need to be tested in the actual circuit to verify the appropriateness of the selected fuse. This verification shall include testing under normal and fault conditions to ensure that the selected fuse is protecting the circuit being protected.








